For this task, I have conducted research in to the body’s healing process. Understanding this process, and factors that may effect it, will give me an additional insight that will help me create extremely realistic wounds, using Special Effects Makeup- during my final assessment
From start to finish, the body’s healing process can take between two weeks, and three years – depending on the size and severity of the incident.
Applying pressure to a wound helps to stop bleeding by pushing the blood vessels together, slowing the blood flow, and helping clots to form.
When the body is injured, its healing process kick-starts into motion. There are many factors that may vary the speed and effectiveness of this process, which I have documented below.
Hemostasis (Normal healing process)
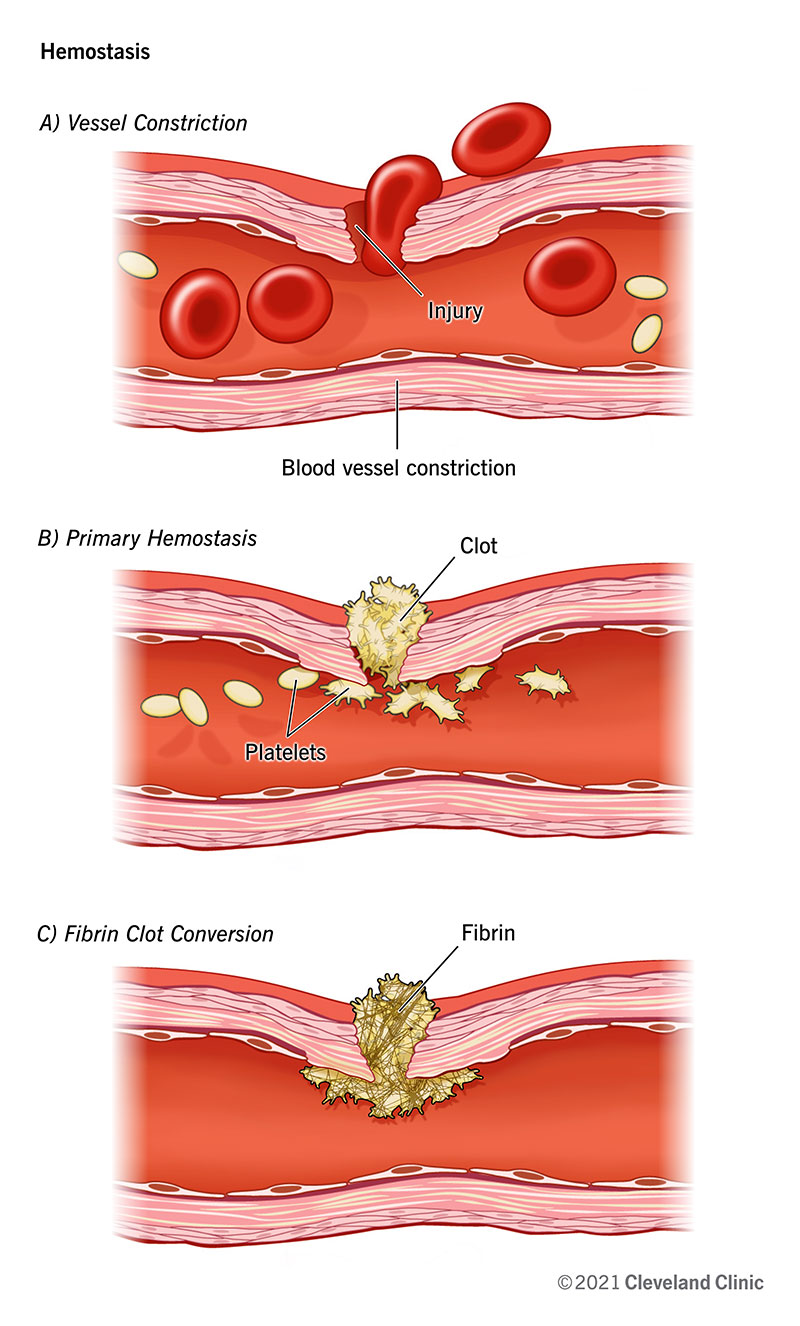
When the skin is scraped, cut or punctured, you are more than likely going to bleed. In normal circumstances, within a few minutes – or even seconds – your red blood cells will begin to clump together, and clot, protecting the wound and preventing further blood loss. The blood clots will in time turn to scabs, as they dry.
Once a wound is closed, the blood vessels begin to slightly open, allowing fresh nutrients, and oxygen, access to the blood. Blood borne oxygen is a vital component in this process, and is essential for the wound to heal effectively. White blood cells are responsible for protecting a wound, by fighting infection and overseeing the bodily repair process. These cells may clean the wound, from the inside, sometimes resulting in a clear fluid that may become visible around the site of injury.
Blood cells help to rebuild the new tissue, healing the body back to almost 100% of what it was before. This process may result in scarring that should fade over time.
Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability – excess blood clotting)

Some people may suffer from conditions that cause thrombophilia – meaning the blood clots too much, or too fast/easily.
These conditions can cause serious complications, as clots could develop in important areas of the body (your internal organs), or get stuck in the blood vessels around the body – causing potentially life threatening conditions.
Furthermore, excess blood clotting causes thickened blood, longer healing processes, and skin that is prone to unexplainable bleeding and bruising. When injured, blood clots may block arteries, making their response times slower. Therefore, this condition could cause excessive bleeding.
Hypocoagulability (lack of blood clotting)
On the opposite end of the scale, some may suffer from conditions causing a lack of blood clotting. Hypercoagulability is used to describe blood that does not close enough, or form clots fast enough.
Those that suffer with this condition are at high risk of extreme blood loss. As the blood doesn’t clot enough, it takes much longer for a person’s bodily healing processes to start, meaning even the most minor injuries could cause potentially dangerous amounts of blood loss. This also causes a greater risk of injuries to internal organs, and blood vessels, which in turn could lead to internal bleeding.
Blood loss is an extremely dangerous factor for those who suffer this condition. Having thin blood, means the blood can travel much faster, causing potentially fatal outcomes.
Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding can be caused by blunt force, or penetrating trauma.
In most cases, internal bleeding leads to life changing, and potentially fatal outcomes.
Internal bleeding can cause; swelling and pain in the abdominal region, lightheadedness/ dizziness/ nausea due to blood loss, ecchymosis (a deep purple coloring of the skin) and extreme swelling.
